FORTIFICATION OF A WINDOWS SERVER ENVIRONMENT by Fernando
Background
In this activity we are asked to put into practice the knowledge acquired in the first topic of the operating systems security course. We are asked to deploy a domain controller and a computer attached to it, on which we will apply different security measures, both at the domain level to this one in which we will apply different security measures, both at domain level and in the as well as on the computer itself. For this purpose, the laboratory has been carried out on a Windows Server 2016 virtual machine and a Windows Server 2016 virtual machine. Windows Server 2016 virtual machine and a Windows 7 client machine.
DEPLOYMENT OF A DOMAIN CONTROLLER
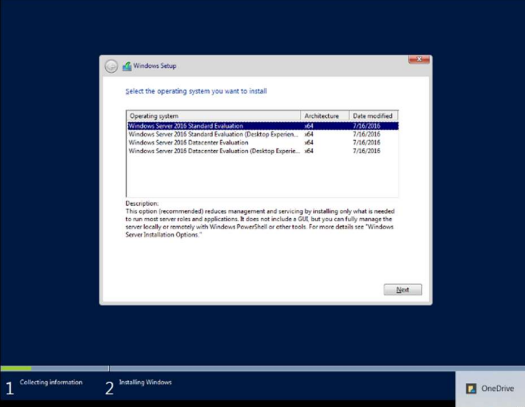
We proceeded with the download of the Windows Server 2016 ISO, which we will use for the implementation of the for the laboratory implementation of the requested activity.
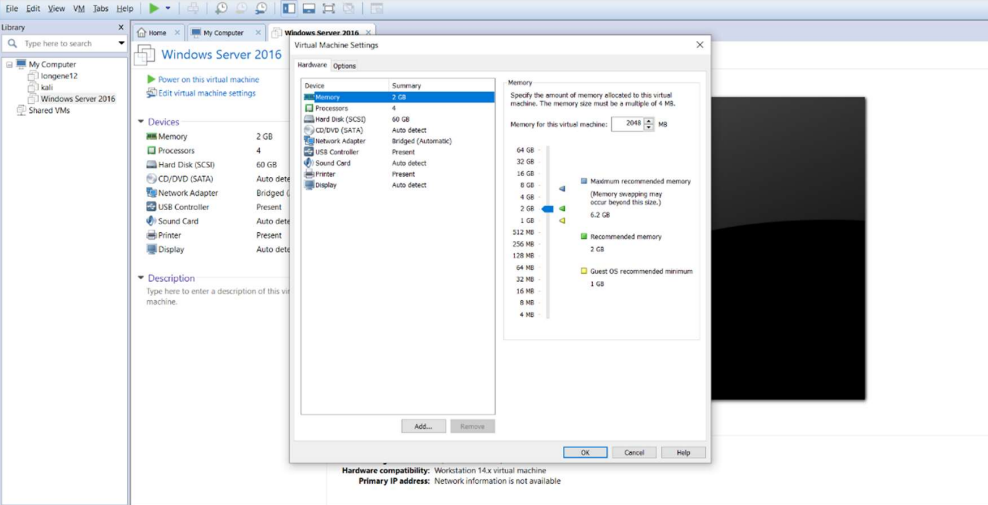
Then we proceed with the virtual hardware configuration that we will use to deploy our virtual machine. be able to deploy our virtual machine.
For the present laboratory we used the operating system Windows Server 2016 Datacenter (Desktop experience) and on which we will solve the different activities.
Adding Roles and Features
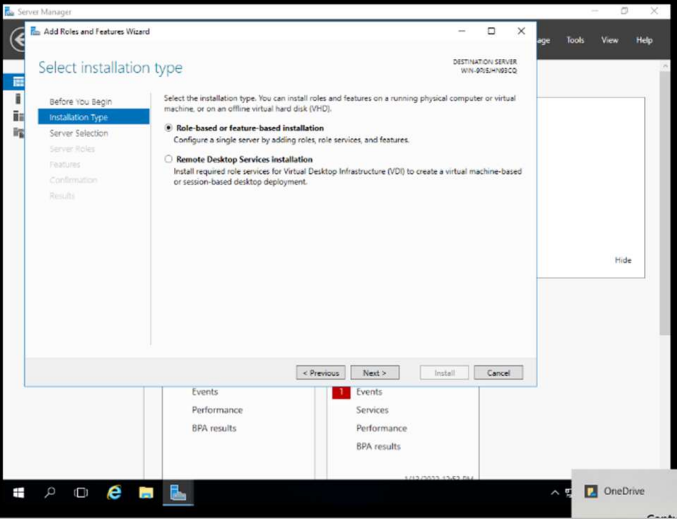
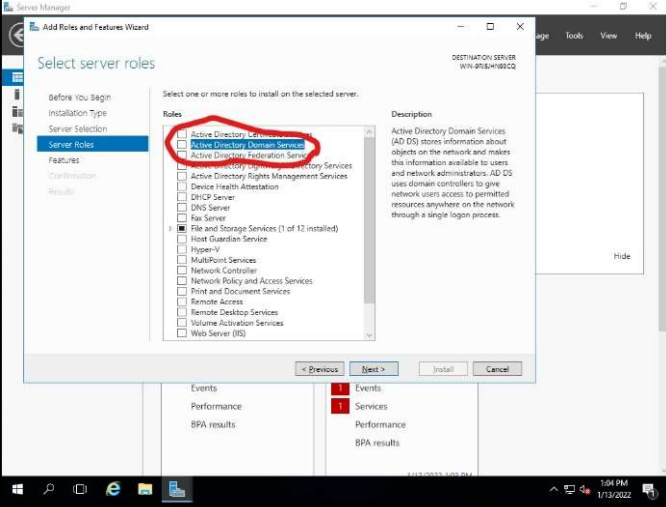
First, we access the Windows Server 2016 server with the local administrator account and proceed to add the necessary roles through the server administration panel, specifically the ACTIVE DIRECTORY DOMAIN SERVICES role.
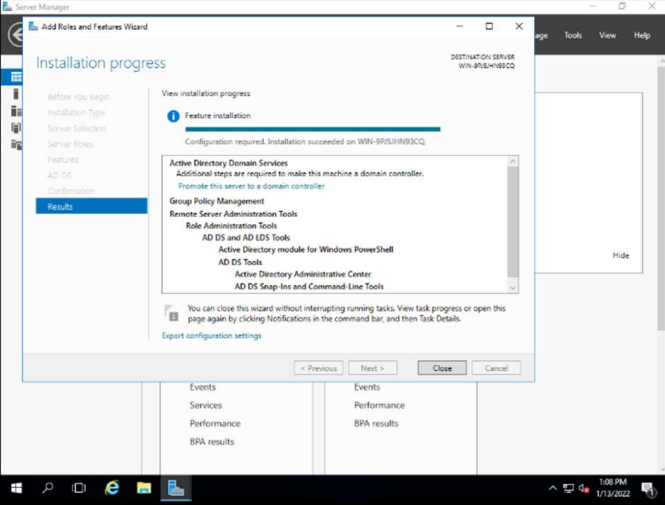
Select the desired role and continue with the wizard. We continue with the wizard confirming the installation of roles and features necessary to implement a server that is a domain controller. necessary to implement a server that is a domain controller, after the restart we must configure the controller. restart we will have to configure the controller.
We see that the installation has finished correctly:
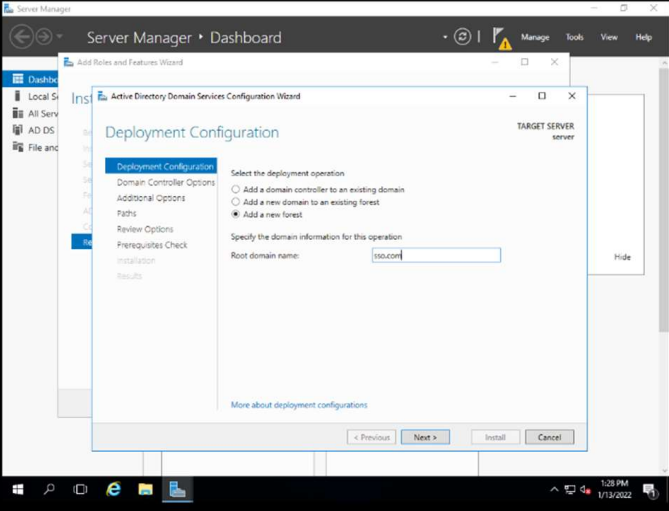
We promote the domain controller
After the reboot, we will configure the domain controller as indicated in the activity, with the domain name sso.com
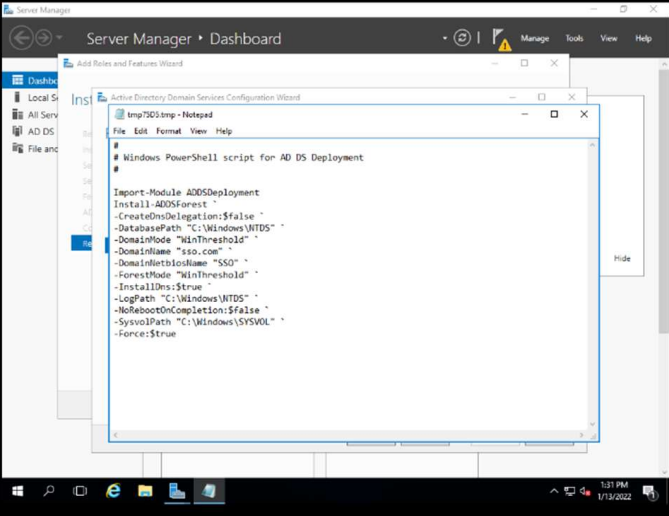
After giving the options this script is created in case you want to autogenerate in another server.
WINDOWS 2012 SERVER CONFIGURATION
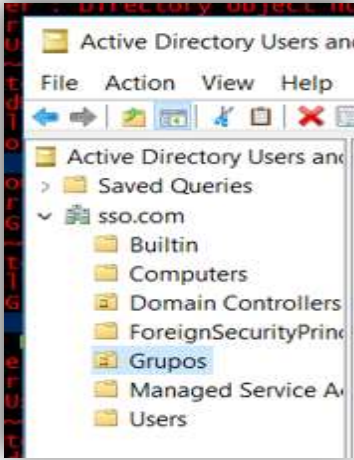
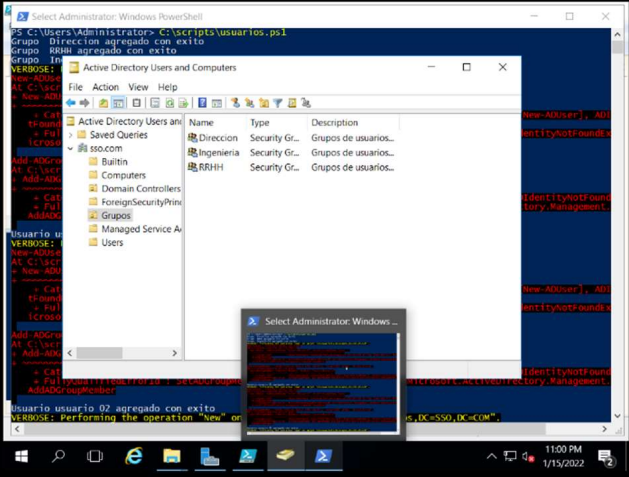
We have chosen to create an OU (Organizational Unit) named “Groups” within the active directory, for better management of groups and user accounts.
Creation of workgroups
The script is created on disk C, “C:/scripts/users.ps1”.
The first part of the script is used to create the Departments (groups) requested in the activity and the second part of the script is used to create the users. the activity and with the second part of the script the users are generated.
Powershell user creation
#Write-Host 'Hello from PowerShell!'
Import-Module ActiveDirectory
$data = @('Direccion','RRHH','Ingenieria') #arreglo de grupos
$cont = 0
#Get-ADDomainController -filter {IsGlobalCatalog -eq $True}
while($cont -lt 3)#este loop sirve para agregar los grupos basado en los arreglos
{
$grupo=""+$data[$cont]
New-ADGroup -Name $grupo -SamAccountName $grupo -GroupCategory Security -GroupScope Global -DisplayName "Departamento de $grupo" -Path "OU=Grupos,DC=sso,DC=com" -Description "Grupos de usuarios de $grupo"
Write-Host "Grupo "$grupo" agregado con exito"
$cont++
}
$cont = 0 #reinicializar el contador de grupos en 0 para la asignacion del grupo cuando se agrega un nuevo usuario
#$ou="0U=Grupos,DC=sso,DC=com" Quise usar esta variable para el path pero mandaba error porque termina en :string
#Write-Host (Get-ADDomain).DistinguishedName ver controladores de dominio
$dominio= (Get-ADDomain).DNSRoot #obtener dominio
$usuario="0"
$cont2=1
while($cont2 -le 50) #loop para agregar usuarios sin usar un csv
{# las condicionales -le,-lt,etc estan documentadas en la bibliografia
if($cont2 -lt 10)
{$usuario="0"+$cont2}#si el usuario es menor de 10 se antepone el 0 para mantener los 2 digitos
if($cont2 -ge 10)
{$usuario=$cont2}
$grupo=""+$data[$cont]
$nombre="usuario"+$usuario
$UPN="usuario$usuario@$dominio"
Write-Host $UPN
New-ADUser -SamAccountName $nombre -UserPrincipalName ($UPN) -Name $nombre -DisplayName $nombre -Surname "Apellido$usuario" -GivenName "nombre$usuario" -Department "departamento$usuario" -Description "descripcion del usuario$usuario" -AccountPassword (ConvertTo-SecureString "SSS00-un1ir" -AsPlainText -force) -Path "OU=Grupos,DC=sso,DC=com" -Enabled $true -ChangePasswordAtLogon $true -Verbose
<# $NewUserParams = @{
Name = $nombre
userprincipalname = $UPN
givenname = $nombre
surname = "Apellido"+$nombre
displayname = $nombre
SamAccountName = $nombre
path = $ou
Department = $grupo
AccountPassword = ConvertTo-SecureString 'SSS00-un1ir' -AsPlainText -Force
Enabled = $true
ChangePasswordAtLogon = $true
}New-ADUser @NewUserParams #>
Add-ADGroupMember -Identity $grupo -Members $nombre #asignar el usuario a un grupo
Write-Host "Usuario usuario"$usuario" agregado con exito"
if($cont2 -eq 10)#al llegar al usuario nro 10 cambia de grupo de Direccion a RRHH
{$cont++}
if($cont2 -eq 30)#al llegar al usuario nro 10 cambia de grupo de RRHH a Ingenieria
{$cont++}
$cont2++
}
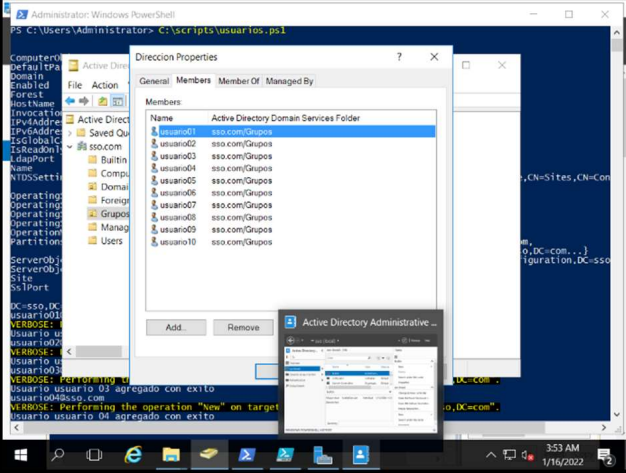
Checks whether the users were created successfully and whether the users were assigned to the created group (“Groups”).
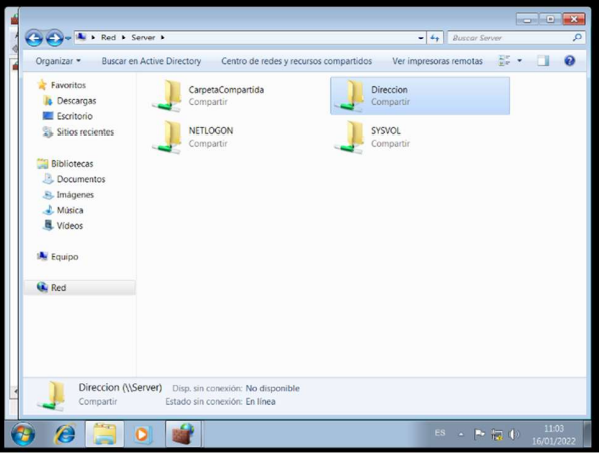
Creating a shared resource
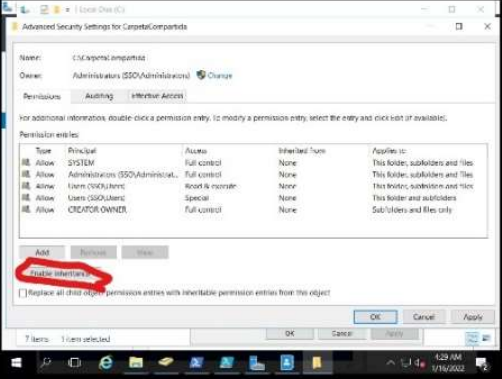
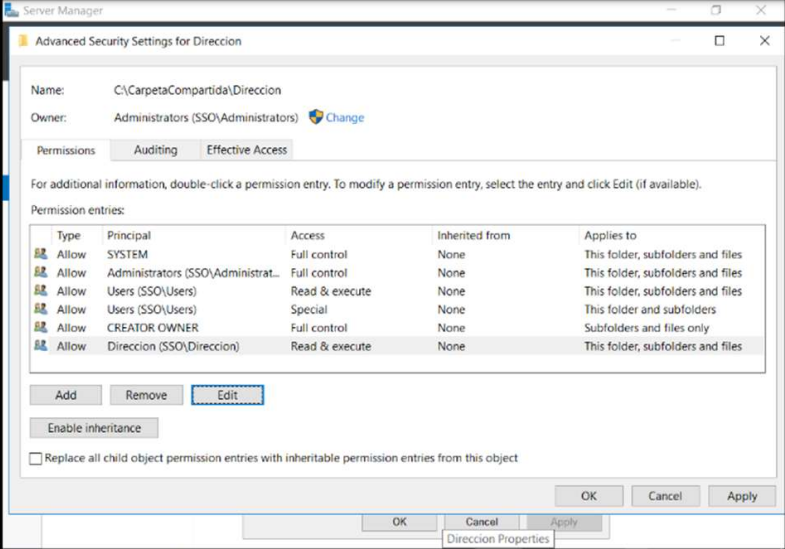
The folder called shared folder was created and in order to avoid problems in the long term the inheritance permissions were deactivated and to this folder the 3 groups were added in “read” permission.
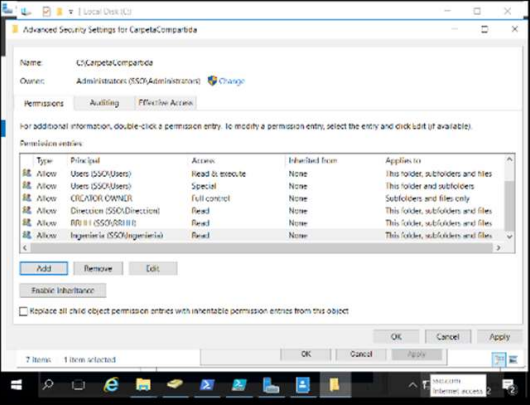
Then 3 folders were created inside this folder and each one was assigned the corresponding permissions, but with read & execute that allows to open, list the content and view the folder.
DOMAIN SECURITY POLICIES
Control Panel and wallpaper
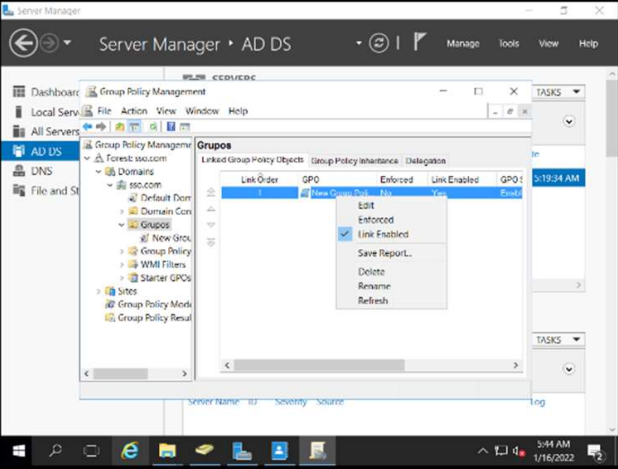
The policy is created in group policy management.
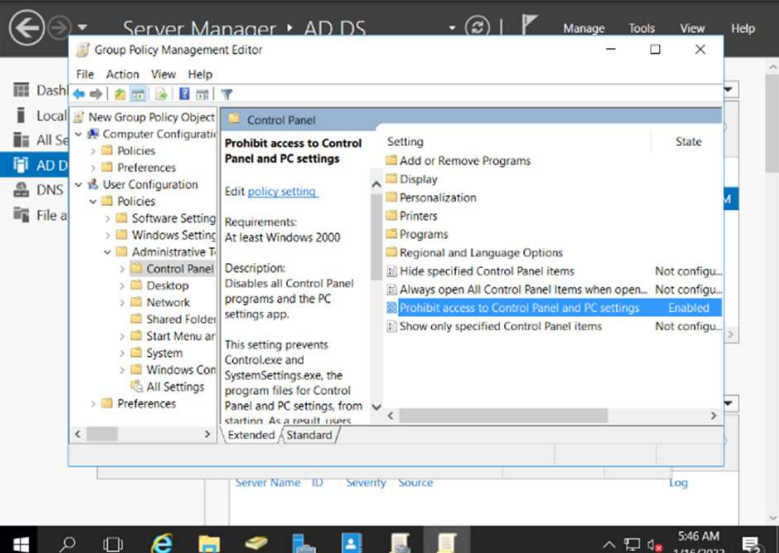
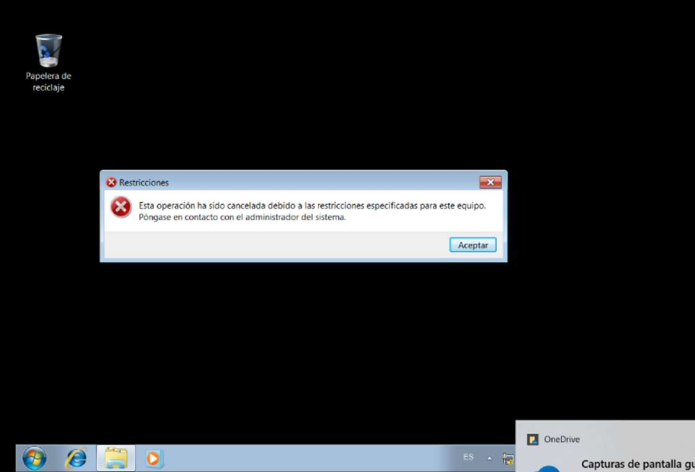
For control panel you give “enable” to this file “Prohibit Access to Control Panel and PC settings”.
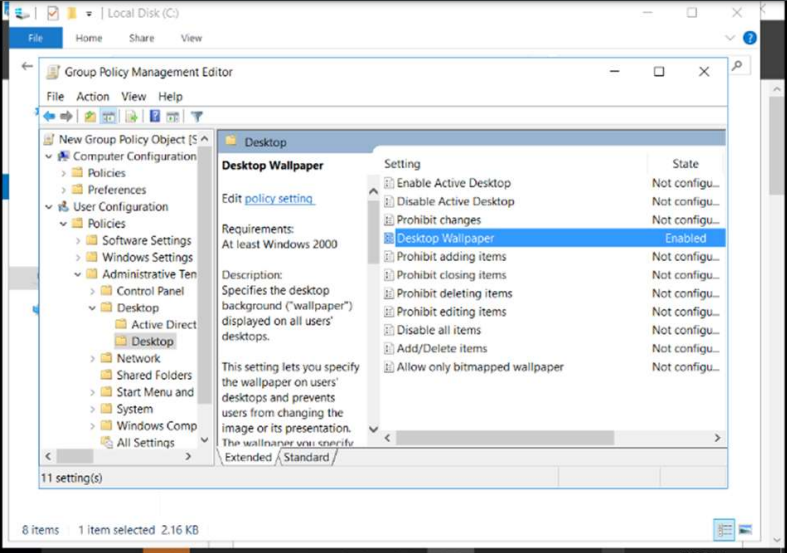
And for desktop wallpaper is this option “Desktop Wallpaper”.
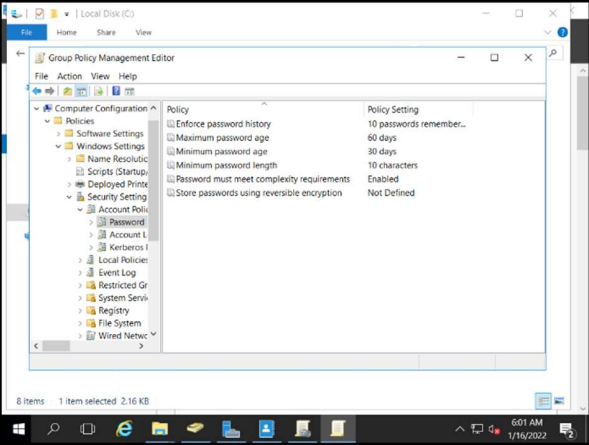
Password policy in the active directory.
Configure the passwords in this way “Minimum password lenght” ensures that the minimum password size if it is to be changed is 10 and enforce enforces the policy setting Apply password history determines the number of unique new passwords that must be associated with a user account before an old password can be reused.
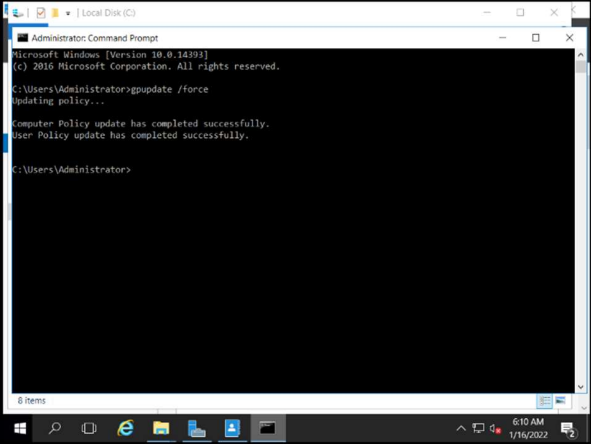
Force policy updates
CHECK CONFIGURATION IN WINDOWS 7
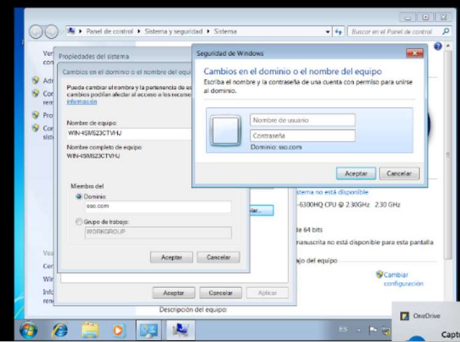
Join Machine to the domain
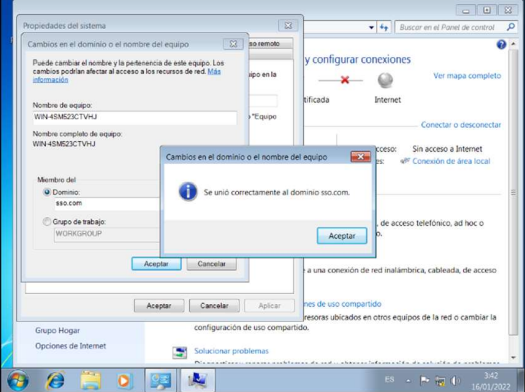
To check all the configurations established in the previous sections we will join a machine with Windows 7 operating system to the domain sso.com for it we accede to the properties of the system and in the tab name of the machine with the button change, we can modify the name and with the credentials of the domain administrator we can join it to the domain.
And when you join, now you are successfully logged in.
Control panel policies and change of image
At this point we can already verify that the security policies have been correctly configured in the equipment and also that the user with which we are accessing has only the necessary permissions for his group of membership.
We also evidenced the generated policy “Desktop Wallpaper”.
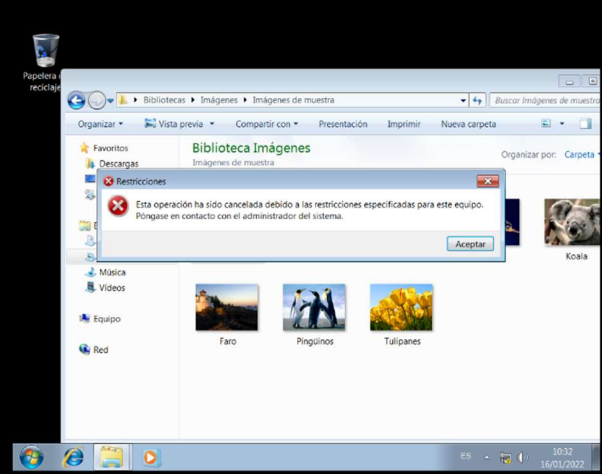
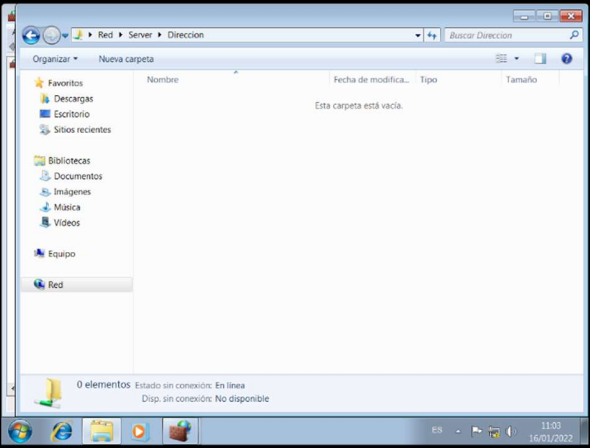
Browse the folders that can be viewed
As you logged in with user01, only the folder address is visible and allows you to open it.
LOCAL SECURITY SETTINGS IN WINDOWS 7
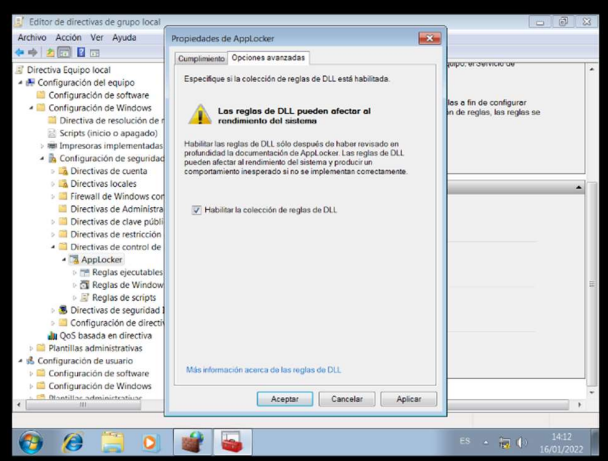
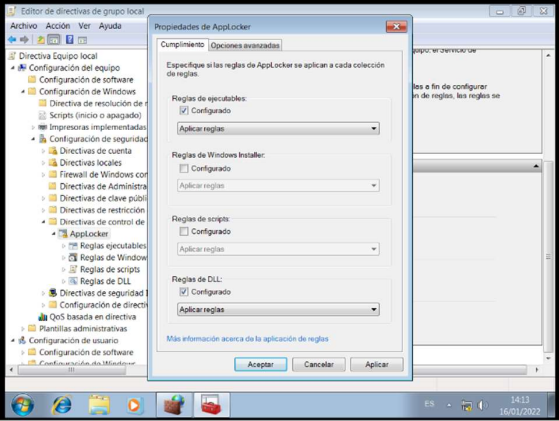
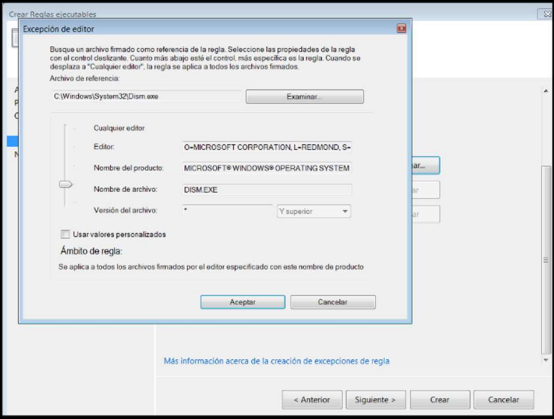
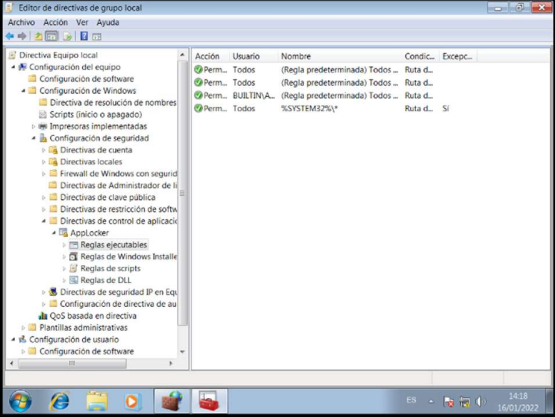
AppLocker Rules
Allow everything from the system32 folder and block a file named “dism.exe”.
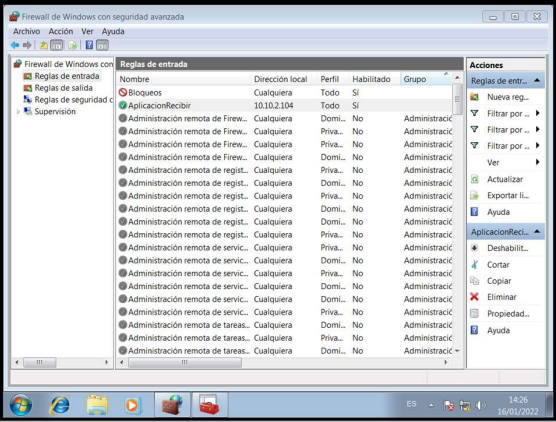
Windows Firewall Configuration
In practice it tells us that we must block all connections to the computer, except for an application that will receive requests to the TCP port from the Local IP 10.10.2.104.
To do this we access the control panel with a local administrator account and in the Windows firewall we enter the advanced firewall settings. We create a new custom inbound rule with the wizard. Here we can see how the configuration of the firewall inbound rules is finally set up. firewall
Summary and references
In this activity the knowledge acquired in the course of Security in Operating Systems has been put into practice. In particular, we have used for its development the notes and slides related to Windows Operating Systems Security both at user and server level, as well as those related to PowerShell and domain policies. We have also used the resources available in Microsoft’s technical support web site and other documents in digital support.
Main References:
Operadores de Comparación con PowerShell Scripting - (salyseo.com)
Powershell:
Everything you wanted to know about arrays (powershellexplained.com)
active directory - New-ADUser -Path syntax? - Server Fault
New-ADUser (ActiveDirectory) Microsoft Docs
Get-ADDomain (ActiveDirectory) Microsoft Docs
PowerShell Array Guide: How to Use and Create (varonis.com)
New-ADGroup (ActiveDirectory) Microsoft Docs
PowerShell Concatenate String Different Examples of Concatenate String
(educba.com)
Adding User In Active Directory gives Error Directory Object not found powershell
(microsoft.com)
New-ADUser error (microsoft.com)
Powershell Add Users Error - Spiceworks
GPO from Group Policy Objects
AEG: How to Create and Link a GPO in Active Directory :: AEG: How to Create and
Link a GPO in Active Directory :: GlobalSign Support
Deploy Desktop Background Wallpaper using Group Policy (prajwaldesai.com)
Minimum Password Length auditing and enforcement on certain versions of Windows
(microsoft.com)
Applocker :%SYSTEM32% xxx123yyy.DLL was prevented from running.
(microsoft.com)
Firewall :How to Create Advanced Firewall Rules in the Windows Firewall
(howtogeek.com)